Create and Construct
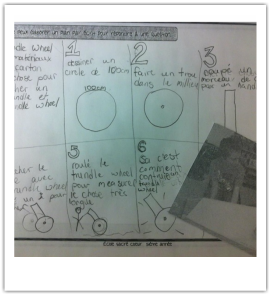
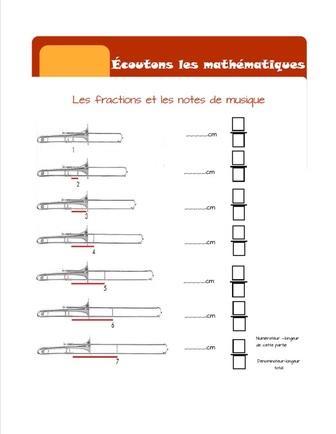
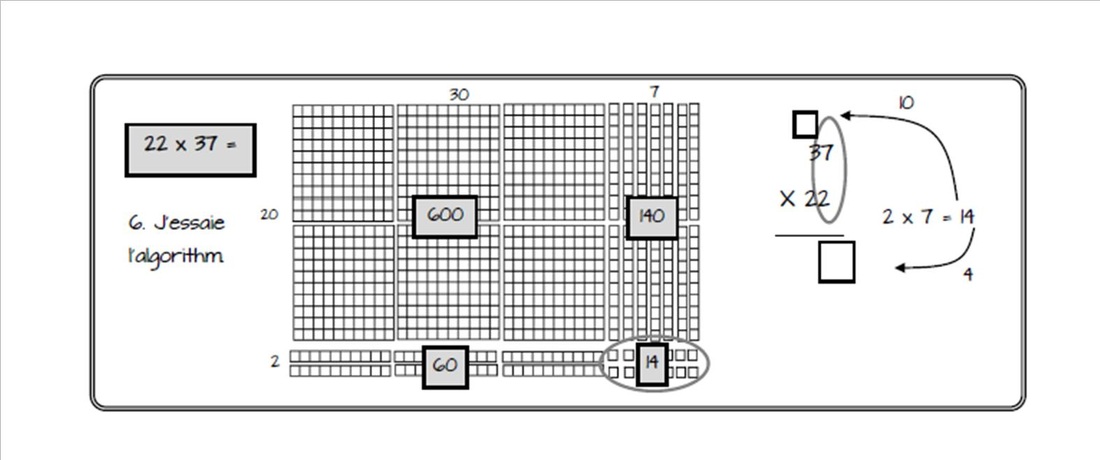
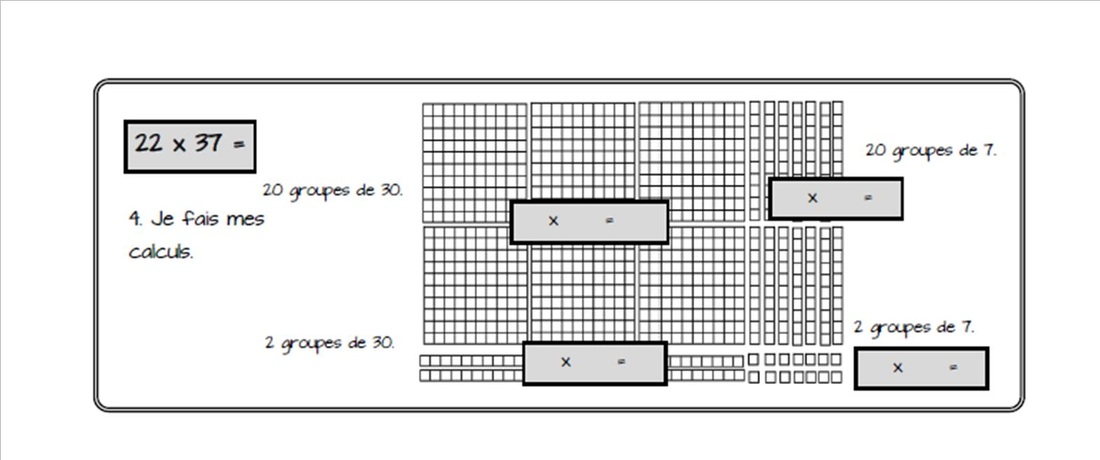
Students are encouraged to experiment with new strategies, create unique processes, construct models, draw sketches, build prototypes, and pursue new paths. Their plans are adjusted as needed and include creative and innovative ideas that arise along their learning paths. Formal processes, formulas and algorithms are first developed through the students' approach to solving a problem. As students notice that the same process can be used in different situations, those that are similar and those that are not, these more formal steps and formulas are derived. The option to use a known formula or to a personal strategy is left to the student. At times, a personl strategy may be more efficient or may open towards further learning opportunities. Reasons for their choice should be explored.
As they go, students monitor and assess the value of their calculations in terms of how each one is contributing to the solution.
As they go, students monitor and assess the value of their calculations in terms of how each one is contributing to the solution.
|
Using a ratio table to deterime the volume of carbon released from cars and the amount of carbon absorbed by trees during photosynthesis.
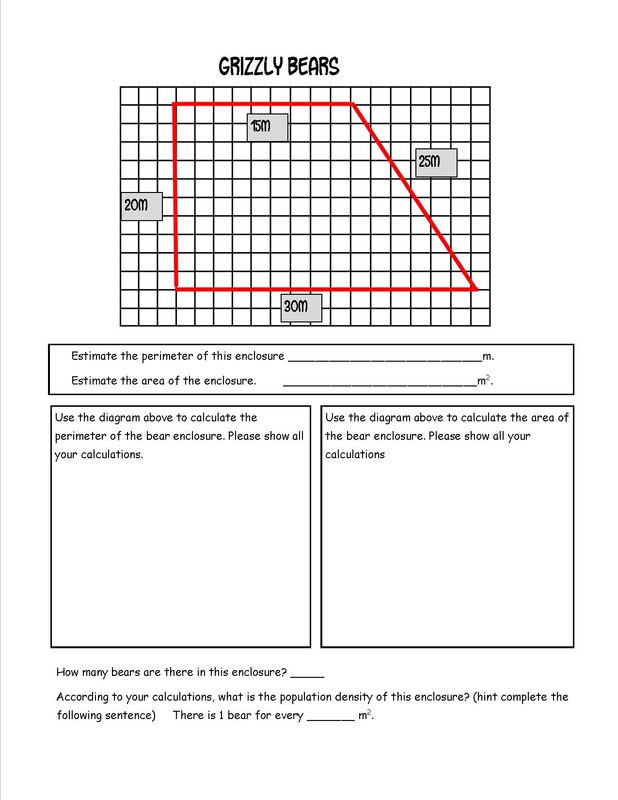
-Using rate (distance and time) to compare our speed with that of a fox. -Using area and perimeter to compare the size of our homes with the size of a pioneer sod house. |